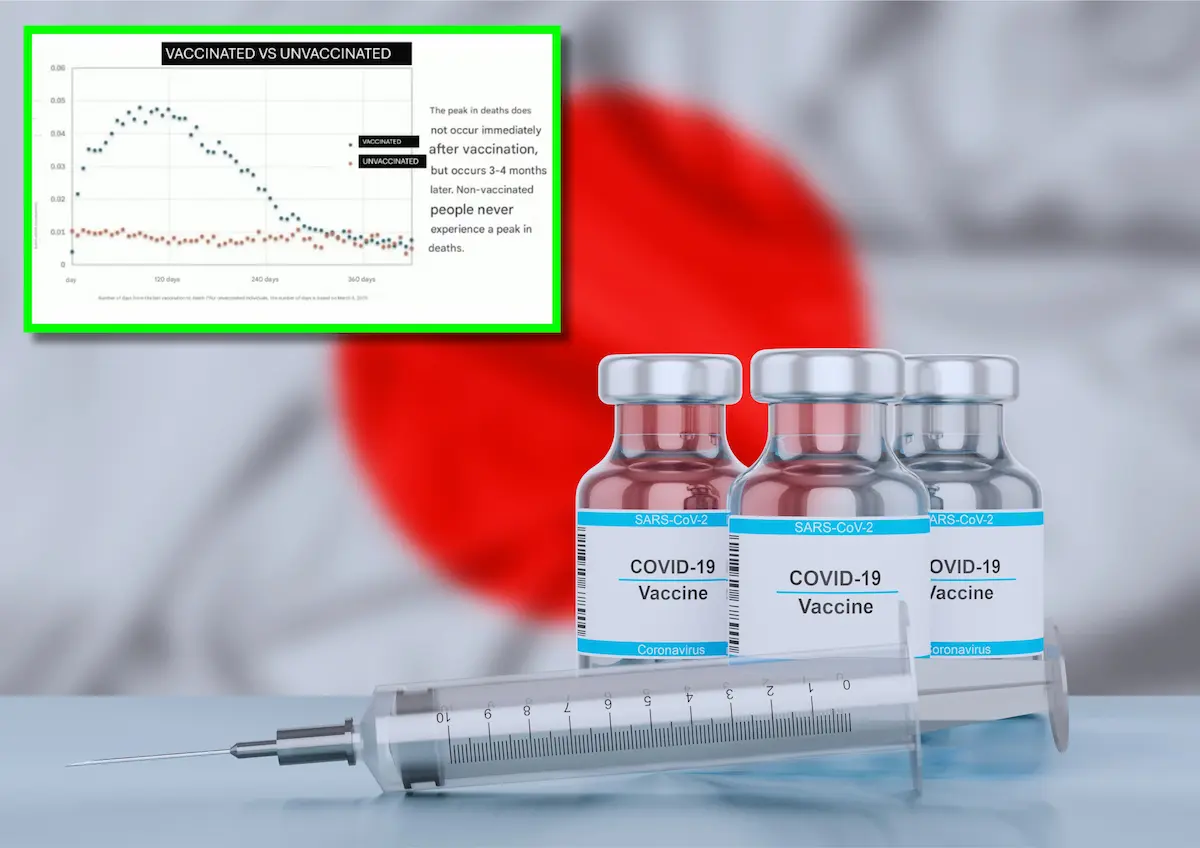
A new Japanese study analyzing data from 18 million citizens suggests a correlation between the number of COVID-19 vaccine doses and earlier mortality peaks(photo-X-The Vigilant Fox)
The Japanese Study That Shook the Silence
In June 2025, a comprehensive study conducted by researchers including Dr. Murakami of Tokyo Science University analyzed health data from over 18 million Japanese citizens. The Japanese study, published in the Journal of the Medical Association of Japan, reported a notable pattern: individuals who received more COVID-19 vaccine doses appeared to experience earlier peaks in mortality, typically within 90 to 120 days post-vaccination.
The researchers emphasized that while the data shows a temporal association, it does not confirm causation. However, the consistency of the pattern across age groups and regions has prompted renewed scrutiny of mRNA vaccine safety, particularly in light of Japan’s high vaccination rates and relatively low COVID-19 fatality numbers.
The study also highlighted a rise in deaths from cardiovascular disease and estrogen-sensitive cancers, suggesting potential links to immune system modulation following repeated vaccinations. These findings have added fuel to ongoing debates about the long-term effects of mRNA technology.
Scientific Uncertainty and Public Concern
The study’s release has sparked polarized reactions. Some scientists have urged caution, warning against drawing premature conclusions from observational data. Others argue that the sheer scale of the dataset warrants serious attention and further investigation.
Adding to the complexity, a related commentary in Discover Medicine noted that frequent mRNA vaccinations may lead to immunosuppression, citing elevated levels of IgG4 antibodies and increased shingles cases as possible indicators. The commentary also referenced three recent child deaths following routine vaccinations in Japan, though no direct causal link was established.
Japan remains one of the few countries still administering additional mRNA doses, even as many nations have scaled back. This divergence has intensified calls for global data transparency, especially as governments weigh future pandemic preparedness strategies.
What Comes Next: Transparency, Research, and Public Trust
The Japanese government has already compensated over 900 vaccine-related deaths and more than 8,000 serious injuries, including cases of myocarditis and autoimmune disorders. These figures, while small relative to the vaccinated population, underscore the need for robust post-vaccination surveillance.
Experts are now calling for:
- Independent audits of national vaccine safety databases
- Longitudinal studies tracking health outcomes across different vaccine regimens
- Open access to anonymized health data for global peer review
For the public, the key takeaway is not panic but informed vigilance. Vaccines remain a cornerstone of public health, but as with any medical intervention, ongoing evaluation is essential to ensure safety, efficacy, and trust.
Stay updated with the latest news on Rapido Updates. Keep yourself updated with The World, India News, Entertainment, Market, Gadgets, Sports, and many more…