Prostate cancer is a serious health concern for men, yet early detection can significantly improve survival rates (photo source-Wikipedia)
Joe Biden’s prostate cancer diagnosis has sent shockwaves through men over 50, emphasizing the critical importance of regular screenings and early detection. With prostate cancer often developing silently, many are now reassessing their health routines, realizing that standard check-ups alone may not be enough. The revelation has fueled discussions about advanced diagnostic methods, such as MRI screenings and genetic testing, prompting increased awareness and urgency around preventive healthcare. As Biden undergoes treatment, his case serves as a stark reminder that proactive monitoring can make all the difference in survival and quality of life.
Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer among men globally, affecting millions each year. While some cases remain slow-growing and manageable, others can be aggressive and life-threatening. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for early detection and prevention.
In this blog, we’ll explore what prostate cancer is, how it develops, and the latest medical advancements in treating this condition.
Table of Contents
1. What is Prostate Cancer?
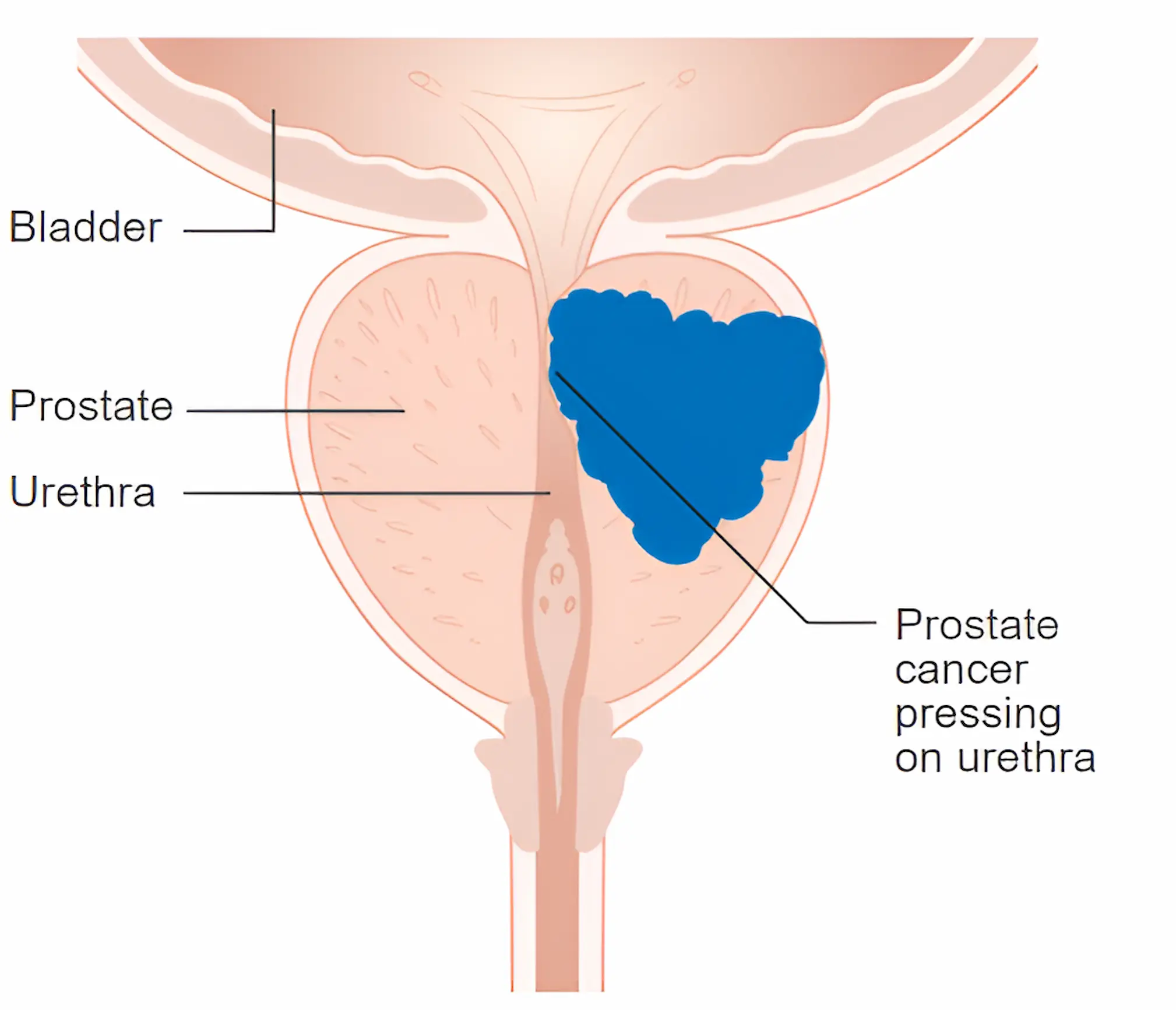
Prostate cancer begins in the prostate gland, a small organ located below the bladder and in front of the rectum. The prostate plays a vital role in producing seminal fluid, which nourishes and transports sperm.
Cancer occurs when cells in the prostate mutate and grow uncontrollably, forming tumors. While some prostate cancers remain localized, others can spread to bones, lymph nodes, and other organs, making treatment more challenging.
2. Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors contribute to the development of prostate cancer:
A. Age
- The risk increases significantly after age 50, with most cases diagnosed in men over 65 years old.
B. Genetics & Family History
- Men with a family history of prostate-cancer are at higher risk.
- Certain genetic mutations, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2, may increase susceptibility.
C. Lifestyle & Diet
- High-fat diets and processed foods may contribute to prostate cancer risk.
- Regular exercise and a healthy diet rich in fruits and vegetables can lower the risk.
D. Ethnicity
- African American men have a higher risk and tend to develop more aggressive forms of the disease.
3. Symptoms of Prostate-Cancer
Prostate cancer often develops silently, with no symptoms in early stages. However, as the disease progresses, men may experience:
- Frequent urination, especially at night
- Weak or interrupted urine flow
- Blood in urine or semen
- Pain in the lower back, hips, or pelvis
- Erectile dysfunction or difficulty urinating
If you experience any of these symptoms, consult a doctor for screening and early detection.
4. Diagnosis & Screening Methods
Early detection is key to successful treatment. Doctors use several screening methods:
A. PSA Test (Prostate-Specific Antigen)
- Measures PSA levels in the blood.
- High PSA levels may indicate cancer but can also be caused by other conditions.
B. Digital Rectal Exam (DRE)
- A doctor checks for abnormal growths in the prostate.
C. MRI & Biopsy
- MRI scans provide detailed images of the prostate.
- A biopsy confirms cancer by analyzing prostate tissue.
Regular screenings are recommended for men over 50, or earlier for those with high-risk factors.
5. Treatment Options for Prostate Cancer
Treatment depends on the stage and aggressiveness of the cancer. Common options include:
A. Active Surveillance
- For slow-growing cancers, doctors may monitor the condition without immediate treatment.
B. Surgery (Prostatectomy)
- Removes the prostate gland to prevent cancer spread.
- Recommended for localized cancer.
C. Radiation Therapy
- Uses high-energy beams to destroy cancer cells.
- Effective for early-stage and advanced cases.
D. Hormone Therapy
- Blocks testosterone, which fuels prostate cancer growth.
- Used for advanced cases.
E. Chemotherapy & Immunotherapy
- Kills cancer cells or boosts the immune system to fight cancer.
- Used for aggressive and metastatic cancer.
6. Prevention & Lifestyle Changes
While prostate cancer cannot always be prevented, certain lifestyle changes can reduce the risk:
- Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins.
- Exercise regularly to maintain a healthy weight.
- Limit processed foods and red meat consumption.
- Get regular screenings if you’re over 50 or have a family history.
Conclusion
Prostate cancer is a serious but manageable condition, especially with early detection and proper treatment. Understanding the risk factors, symptoms, and available treatments can help men make informed health decisions.
1 thought on “What is Prostate Cancer? Cause Symptom Treatment”